|
|
5 years ago | |
|---|---|---|
| Dockerfile | 5 years ago | |
| LICENSE.txt | 7 years ago | |
| README.md | 5 years ago | |
| docker-compose.yml | 5 years ago | |
| femtoshare.py | 5 years ago | |
| screenshot.png | 7 years ago | |
README.md
Femtoshare
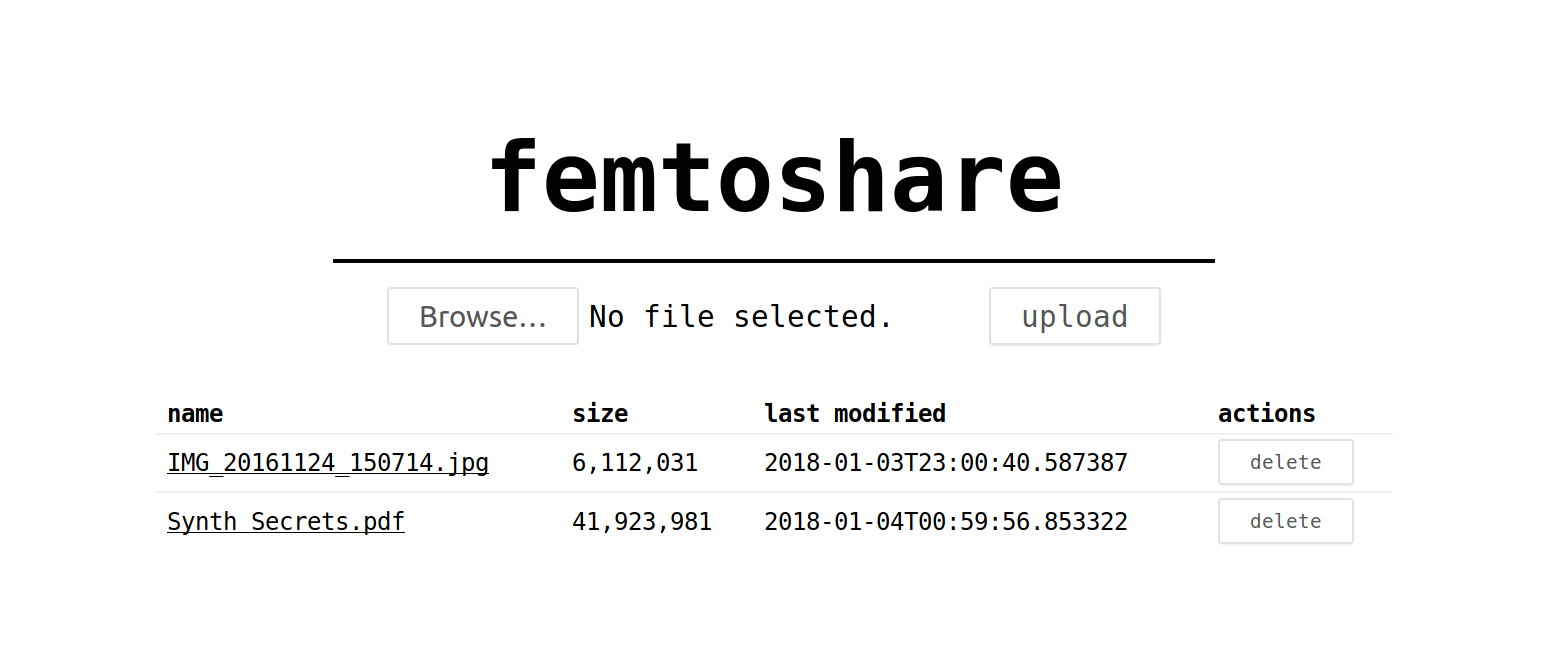
Ultra simple self-hosted file sharing in a single Python script, without any dependencies. All files can be accessed/modified by all users. Don't upload anything secret!
Quickstart: wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Uberi/femtoshare/master/femtoshare.py; chmod +x femtoshare.py; femtoshare.py, then visit http://localhost:8000/ in your web browser.
Options:
$ ./femtoshare.py --help
usage: femtoshare.py [-h] [--port PORT] [--public]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--port PORT local network port to listen on
--public listen on remote network interfaces (allows other hosts to see
the website; otherwise only this host can see it)
Rationale
I often need to send/receive files from untrusted computers. Google Drive can be used for receiving, but not sending - I don't care about people seeing the files, but I do care about not revealing my account credentials when logging in to upload files.
Services like WeTransfer work for sending, but they often have tiny file size limits and long, hard-to-type file URLs, if they work at all.
I made Femtoshare to fix these issues. It's basically an FTP server that only needs a web browser to browse/download/upload. No file size limits and easily-memorized links, plus no worries about revealing important account credentials! A site-wide password is easily added to keep out the most unsophisticated attackers.
Deployment
Minimal public-facing deployment: wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Uberi/femtoshare/master/femtoshare.py; chmod +x femtoshare.py; ./femtoshare.py --port 1234 --public is visible at http://YOUR_HOST:1234.
For improved security, authentication, and HTTPS support, we can run the script as a systemd daemon and put it behind an Nginx reverse proxy, configured to use HTTP Basic Authentication. Assuming a fresh Ubuntu 16.04 LTS machine:
-
SSH into the machine:
ssh ubuntu@ec2-35-166-68-253.us-west-2.compute.amazonaws.com. -
Run software updates:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade. -
Harden SSH: in
/etc/ssh/sshd_config, changePasswordAuthenticationtonoandPermitRootLogintonoandAllowUserstoubuntu. Restartsshdusingsudo service sshd restart. -
Get requirements:
sudo apt-get nginx openssl. -
Get the code:
sudo mkdir -p /var/www/femtoshare && cd /var/www/femtoshare && sudo wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Uberi/femtoshare/master/femtoshare.py; sudo chmod +x femtoshare.py. -
Set up restricted user:
sudo adduser --system --no-create-home --disabled-login --group femtoshare(there is anobodyuser, but it's better to have our own user in case other daemons also usenobody). -
Set up file storage directory:
sudo install -o femtoshare -g femtoshare -d /var/www/femtoshare/files. -
Set up systemd service to start Femtoshare on boot:
sudo tee /lib/systemd/system/femtoshare.service << EOF [Unit] Description=Femtoshare [Service] Type=simple PrivateTmp=yes User=femtoshare Group=femtoshare ExecStart=/var/www/femtoshare/femtoshare.py Restart=always RestartSec=5 [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target EOF sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl enable femtoshare.service -
Set up a password file for HTTP Basic Authentication:
echo "user:$(openssl passwd -apr1 -salt 8b80ef96d09ffd0be0daa1202f55bb09 'YOUR_PASSWORD_HERE')" | sudo tee /var/www/femtoshare/.htpasswd -
Set up Nginx as a reverse proxy with HTTP Basic Authentication:
sudo tee /etc/nginx/conf.d/femtoshare.conf << EOF server { listen 80; server_name ~.; # HTTP Basic Authentication auth_basic "Log in with username 'user' to access files"; auth_basic_user_file /var/www/femtoshare/.htpasswd; # serve directory listing location = / { # HTTP Auth Just For POST Requests (This will allow users toread files but they won't be able to upload or delete anything) # limit_except GET HEAD { # auth_basic "Log in with username 'user' to access files"; # auth_basic_user_file /var/www/femtoshare/.htpasswd; # } proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8000; client_max_body_size 1000M; } # serve uploaded file location ~ /.+ { root /var/www/femtoshare/files; } } EOF -
Set up HTTPS with Let's Encrypt:
export LC_ALL="en_US.UTF-8"; export LC_CTYPE="en_US.UTF-8"; sudo wget https://dl.eff.org/certbot-auto && sudo chmod a+x certbot-auto && sudo ./certbot-auto --nginx --debug -
Set up twice-daily certificate renewal cronjob with Let's Encrypt: add
23 0,12 * * * PATH=/home/ubuntu/bin:/home/ubuntu/.local/bin:/home/ubuntu/bin:/home/ubuntu/.local/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/snap/bin /var/www/femtoshare/certbot-auto renew >> /var/www/femtoshare/letsencrypt-renew-certificate.log 2>&1in the root crontab withsudo crontab -e(settingPATHis necessary in order to get Nginx config updates to work). -
Start Femtoshare and Nginx:
sudo systemctl start femtoshare.serviceandsudo service nginx restart. -
Allow incoming and outgoing HTTP and HTTPS traffic through the firewall.
License
Copyright 2018-2018 Anthony Zhang (Uberi).
The source code is available online at GitHub.
This program is made available under the MIT license. See LICENSE.txt in the project's root directory for more information.